Quest of Code: AI Usage for Thinkers
Educational curriculum focusing on responsible AI usage and critical thinking skills


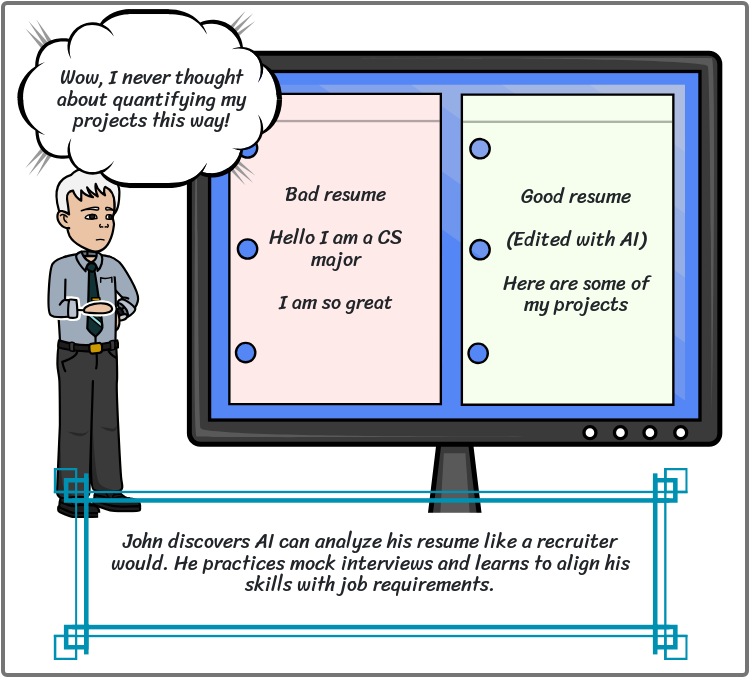
1 - Resume review and interview prep - Saanvi
-
AI-assisted resume critique
-
ATS systems: keyword matching, common rejection triggers, formatting requirements
-
STAR method and quantification: transforming bullets into achievement statements with metrics
-
Resume tailoring: analyzing job descriptions, customizing summaries, strategic keyword integration
-
ATS-friendly formatting: section order, fonts, white space, file formats
-
Resume scanner: Upload for instant ATS score with visual heat map of strengths/weaknesses
-
Bullet transformer: Input info, get 3-5 STAR-formatted versions with metrics
-
Job matcher: Paste posting, get color-coded gaps and specific edit suggestions
-
Keyword optimizer: Real-time ATS score updates as you add industry keywords
-
Transform sample resume for target job (60 min): identify 5 issues, rewrite 5 bullets with STAR/metrics, add 10 keywords, achieve 85+ ATS score
-
Submit before/after versions + 300-word explanation
-
Pass: 75% (ATS 25%, quantification 25%, keywords 20%, alignment 20%, formatting 10%)
-
Mock interview simulations
-
Interview question types: behavioral, technical, situational, culture fit
-
STAR method structure and timing (30 sec-2 min responses)
-
Company research and connecting experience to company needs
-
Handling difficult questions: weaknesses, gaps, salary negotiation
-
Question generator: 20 questions by role/industry/level with difficulty slider
-
Recording studio: Video/audio with timer, transcript, filler word counter
-
AI feedback: Scores for STAR structure, relevance, specificity, confidence (0-10)
-
Company chatbot: Instant brief on mission, news, likely interview questions
-
45-minute mock interview (48 hours prep): Introduction (2 min), 4 behavioral questions (20 min), 3 technical questions (15 min), 1 curveball (5 min), your questions (3 min)
-
Delivery: Video, live AI, or typed responses
-
Pass: 70% (STAR 20%, relevance 20%, specificity 20%, delivery 15%, company knowledge 15%, questions 10%)
-
Job market alignment
-
Skills taxonomy and transferable skills across industries
-
Labor market data: BLS, LinkedIn reports, emerging technology trends
-
Competitive benchmarking and unique value proposition development
-
Learning ROI and strategic job search: quality vs. quantity, networking timing
-
Skills gap visualizer: 100+ skills checklist, input role for priority-ranked gaps
-
Industry dashboard: Salary trends, job volume, top companies, hot skills by role
-
Learning path generator: AI suggests courses/projects with timeline and cost
-
Job search command center: Track applications, 30 target companies, automated reminders
-
90-day career strategy portfolio (3-4 hours): Skills audit with 3 development priorities (30 min), market research of 10 jobs with trend analysis (45 min), competitive positioning statement (30 min), learning roadmap (45 min), 25 target companies with outreach plan (60 min)
-
Submit: Portfolio PDF, Excel tracking, tool screenshots
-
Pass: 75% (skills 15%, research 20%, positioning 15%, roadmap 25%, strategy 20%, presentation 5%)
2 - How to properly prompt (prompt engineering) making sure you actually give it the correct scenario when talking with it - Mihir
- Prompt structure fundamentals
What to Cover:
-
The basic anatomy of an effective prompt (context, task, constraints, format)
-
How to provide sufficient background information
-
Specifying your role and the AI’s role
-
Defining clear objectives and expected outputs
-
Setting parameters (length, tone, audience, style)
-
Examples of weak vs. strong prompts for academic tasks
Interactive Elements:
-
Text areas where students write example prompts
-
Side-by-side comparison of “before” and “after” prompt improvements
-
Fill-in-the-blank exercises for building complete prompts
-
Dropdown menus to identify missing prompt components
Sample Exercise Structure:
-
Weak Prompt Example: [Show poorly constructed prompt]
-
Student Task: Identify what’s missing [Checkboxes for: Context, Clear objective, Constraints, Format]
-
Improved Prompt: [Text area for student to rewrite]
-
Save/Load functionality for student work
-
Iterative refinement
What to Cover:
-
Understanding that first prompts rarely give perfect results
-
How to analyze AI responses for gaps or misunderstandings
-
Techniques for follow-up questions and clarifications
-
Adjusting your prompt based on what didn’t work
-
When to start over vs. when to refine
-
Building on previous responses in a conversation
Interactive Elements:
-
Multi-step exercise showing a conversation thread
-
Students identify where the prompt went wrong
-
Practice writing follow-up prompts to improve results
-
Before/after examples of iterative improvements
Sample Exercise Structure:
-
Initial Prompt & Response: [Show example interaction]
-
Problem Identification: What went wrong? [Multiple choice or checkboxes]
-
Your Refinement Prompt: [Text area]
-
Comparison: See suggested refinement approach
-
Save/Load functionality for student work
-
Edge-case prompting
What to Cover:
-
Recognizing AI limitations and knowledge cutoff dates
-
Handling ambiguous or unclear assignment requirements
-
What to do when AI provides conflicting information
-
Prompting for verification and source checking
-
Dealing with topics where AI shouldn’t provide definitive answers
-
Understanding when AI might hallucinate or provide outdated info
-
How to prompt AI to help clarify your own thinking rather than do thinking for you
Interactive Elements:
-
Scenario-based challenges presenting edge cases
-
Students choose appropriate response strategies
-
Practice prompts for handling unusual situations
-
Checkboxes for identifying when to verify information independently
Sample Exercise Structure:
-
Edge Case Scenario: [Present problematic situation]
-
Identify the Issue: [Dropdown or multiple choice]
-
Your Approach: How would you handle this? [Text area]
-
Best Practice: [Show recommended approach]
-
Save/Load functionality for student work
-
Ethical prompting
What to Cover:
-
The line between appropriate assistance and academic dishonesty
-
Prompts that maintain academic integrity vs. those that violate it
-
How to use AI as a learning tool rather than a shortcut
-
Transparency and disclosure requirements
-
Understanding what constitutes your own work
-
Institutional policies on AI usage
-
The difference between getting help understanding vs. having work done for you
Interactive Elements:
-
Ethical scenario analysis with student judgments
-
Creating pairs of ethical vs. unethical prompts for the same task
-
Reflection questions about learning vs. completion
-
Pledge or commitment to ethical AI usage
Sample Exercise Structure:
-
Scenario: [Present academic situation involving AI]
-
Is this appropriate? [Radio buttons: Yes/No/Depends]
-
Explain your reasoning: [Text area]
-
Create Ethical Alternative: Write a better prompt [Text area]
-
Save/Load functionality for student work
3 - Importance of Gemini integrations- Eshika
-
Cross-platform synergy:
-
Unified ecosystem access: Gemini integrations enable seamless connectivity across Google Workspace apps including Gmail, Docs, Sheets, Drive, and Meet, allowing users to leverage AI capabilities without switching between platforms
-
Contextual awareness: The integration allows Gemini to access and understand context from multiple sources simultaneously, such as referencing email threads while drafting documents or analyzing spreadsheet data during presentations
-
Workflow automation: Users can automate repetitive tasks across platforms, such as summarizing meeting transcripts in Docs, extracting action items from emails, or generating reports from Sheets data
-
Real-time collaboration enhancement: Gemini can assist multiple team members simultaneously across shared documents, providing suggestions and insights that improve collaborative workflows
-
Mobile and desktop consistency: Integrations ensure Gemini functionality remains consistent whether users access Google Workspace through web browsers, mobile apps, or desktop applications
-
Security and compliance
-
Enterprise-grade data protection: Gemini integrations inherit Google Workspace’s security infrastructure, including encryption at rest and in transit, ensuring sensitive data remains protected during AI processing
-
Access control and permissions: The integration respects existing Google Workspace permission structures, ensuring Gemini can only access data that users are authorized to view or modify
-
Compliance with regulations: Gemini integrations support compliance with standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2, making them suitable for regulated industries like healthcare, finance, and education
-
Data residency options: Organizations can control where their data is processed and stored, maintaining compliance with regional data sovereignty requirements
-
Audit trails and monitoring: Administrators can track Gemini usage patterns, monitor data access, and maintain comprehensive audit logs for security and compliance purposes
-
No training on customer data: Google’s commitment to not training Gemini models on customer workspace data helps protect proprietary information and trade secrets
-
Use cases in education and productivity
-
Research and content creation: Students and educators can use Gemini to summarize research papers, generate study guides, create lesson plans, and draft essays with properly structured arguments
-
Data analysis and visualization: Professionals can quickly analyze datasets in Sheets, generate insights, create visualizations, and produce executive summaries without extensive data science expertise
-
Meeting productivity: Gemini can transcribe meetings in real-time, generate summaries, extract action items, and create follow-up emails automatically in Gmail
-
Email management: Users can draft professional emails, summarize long email threads, suggest appropriate responses, and prioritize inbox items based on importance
-
Presentation development: Gemini assists in creating compelling presentations by generating outlines, suggesting design improvements, and creating speaker notes from existing content
-
Language translation and localization: Educators and global teams can translate documents, adapt content for different audiences, and ensure cultural appropriateness across materials
-
Personalized learning: Gemini can adapt explanations to different learning levels, provide additional practice problems, and offer tutoring-style support for complex topics
-
Limitations and fallback strategies
-
Accuracy concerns: Gemini may occasionally produce inaccurate or outdated information; users should verify critical facts and implement fact-checking procedures for important documents
-
Context window restrictions: Large documents or datasets may exceed processing limits; fallback strategies include breaking content into smaller chunks or summarizing sections before analysis
-
Language and domain limitations: Performance varies across languages and specialized domains; users should maintain human oversight for technical, legal, or medical content requiring domain expertise
-
Internet connectivity dependency: Integrations require stable internet connections; organizations should prepare offline alternatives for critical workflows and maintain local backup documentation
-
Cost considerations: Enterprise-level Gemini integrations may require additional licensing; teams should evaluate ROI and consider tiered access models where only power users need full capabilities
-
Privacy-sensitive scenarios: For highly confidential information, users should disable Gemini integrations or use alternative tools that don’t involve cloud AI processing
-
Integration downtime: Service interruptions can occur; maintain manual workflow processes as backup and communicate contingency plans to teams relying on Gemini features
-
Learning curve: Users need training to use integrations effectively; implement gradual rollout strategies with comprehensive training programs and support documentation
-
Over-reliance risks: Teams may become too dependent on AI assistance; encourage critical thinking and maintain human review processes for quality assurance
4 - Coding with AI - Ansh Kumar (Module 4: Coding with AI)
-
Code generation and debugging
-
Scripting and automation
-
Collaborative coding
-
Security and verification
Module 4: Coding with AI
| Duration: ~1 hour | Level: Intermediate |
Learning Objectives
-
Write effective prompts for code generation
-
Debug code efficiently with AI assistance
-
Verify and secure AI-generated code
Part 1: Code Generation
The SPEC Framework
-
Specific: What exactly should the code do?
-
Platform: Language, version, frameworks
-
Examples: Show input/output samples
-
Constraints: Performance, security, style requirements
Example
Bad: “Write a function to process user data”
Good: “Write a Python function that validates user registration data. Accept dict with username, email, password, age. Validate username (3-20 chars, alphanumeric), email (regex), password (8+ chars, upper+lower+number), age (18+). Return (is_valid: bool, errors: list).”
Part 2: Debugging with AI
4-Step Process
-
Isolate: Minimal reproducible code
-
Describe: Expected vs actual behavior
-
Context: Environment details
-
Tried: What you’ve already attempted
Template
I’m encountering [specific error].
Expected: [what should happen]
Actual: [what happens]
Code: [minimal code]
Error: [full error message]
Environment: [versions]
What I’ve tried:
-
[attempt 1]
-
[attempt 2]
---
## Part 3: Scripting & Automation
### Build Incrementally
1. Core functionality
2. Add validation
3. Add error handling
4. Test each step
---
## Part 4: Security & Verification
### Security Checklist
- [ ] Input validation
- [ ] Parameterized queries (prevent SQL injection)
- [ ] XSS protection
- [ ] Authentication/authorization
- [ ] Secure password storage (bcrypt)
- [ ] Rate limiting
- [ ] HTTPS enforced
- [ ] CSRF protection
- [ ] Secrets in environment variables
### Trust But Verify
For all AI-generated code:
1. \*\*Understand it\*\* - Ask: "Explain this code line by line"
2. \*\*Test it\*\* - Generate edge cases and error tests
3. \*\*Secure it\*\* - Check for vulnerabilities
---
## Quick Reference
\*\*Code Generation:\*\*
Create a [language] [component] that [functionality].
Requirements: [list]
Constraints: [list]
Example: Input → Output
\*\*Debugging:\*\*
Debug: [specific error]
Expected: [behavior]
Actual: [behavior]
Code: [minimal reproduction]
Environment: [details]
\*\*Security Review:\*\*
Security audit this code for:
-
Injection vulnerabilities
-
Auth/authz issues
-
Data protection
-
Configuration problems
Key Takeaways
-
Be Specific: Vague prompts → vague results
-
Iterate: Build incrementally, test frequently
-
Verify: Never trust without testing
-
Understand: If you can’t explain it, don’t use it
-
Secure: Always think security first
Remember: You’re the developer. AI is your tool, not your replacement.
Certificate: AI compliant engineer, AI Readiness Check - Nithika

