Computer Science A
2025 FRQ 4
- FRQ Question 4
- Part A:
- Part B:
- Walkthrough of Part B:
- Code Runner Challenge
- Scoring Guidelines
FRQ Question 4
This question involves reasoning about a number puzzle that is represented as a two-dimensional array of integers. Each element of the array initially contains a value between 1 and 9, inclusive. Solving the puzzle involves clearing pairs of array elements by setting them to 0. Two elements can be cleared if their values sum to 10 or if they have the same value. The puzzle is considered solved if all elements of the array are cleared.
You will write the constructor and one method of the SumOrSameGame class, which contains the methods that manipulate elements of the puzzle.
Analyze the Problem: Walkthrough
2D Grid Puzzle Challenge
Problem Type: 2D Array Simulation
Difficulty: Medium
You are given a two-dimensional integer grid called
puzzle.Each cell initially contains a number from 1 to 9.
Example Grid:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A move consists of selecting one cell and clearing it together with one other cell if:
the two values are equal, OR
the two values sum to 10
Clearing a cell means setting its value to
0.The puzzle is considered solved when every element in the grid is
0.
Mental Model
Think of the puzzle as a grid-search problem.
You always begin with a specific cell and then scan other cells in the grid to find a valid partner. If a partner is found, both cells are cleared at the same time.
Each part of the problem focuses on a different responsibility:
- Part A initializes the grid correctly.
- Part B searches the grid and conditionally modifies it.
Part A:
Write the constructor for the SumOrSameGame class. The constructor initializes the instance variable puzzle to be a two-dimensional integer array with the number of rows and columns specified by the parameters numRows and numCols, respectively. Array elements are initialized with random integers between 1 and 9, inclusive, each with an equal chance of being assigned to each element of puzzle.
Note: When an element of the two-dimensional array is accessed, the first index is used to specify the row and the second index is used to specify the column
Walkthrough of Part A:
The constructor is responsible for creating the puzzle grid.
It must:
- Initialize a two-dimensional array with the given number of rows and columns.
- Assign every cell a random integer between 1 and 9, inclusive.
- Ensure that each value has an equal probability of being chosen.
You may assume that the number of rows and columns provided are always greater than zero.
Checkpoint: Before writing the constructor, ask yourself:
- How many times should the grid be traversed?
- What guarantees that every value is between 1 and 9?
- Why is a nested loop required instead of a single loop?
Part B:
Write the clearPair method, which takes a valid row index and valid column index as its parameters. The array element specified by those indices, which has a value between 1 and 9, inclusive, is compared to other array elements in puzzle in an attempt to pair it with another array element that meets both of the following conditions.
- The row index of the second element is greater than or equal to the parameter row.
- The two elements have equal values or have values that sum to 10.
If such an array element is found, both array elements of the pair are cleared (set to 0) and
the method returns true. If more than one such array element is found, any one of those identified array elements can be used to complete the pair and can be cleared. If no such array element is found, no changes are made to puzzle and the method returns false.
The following table shows the possible results of several calls to clearPair.
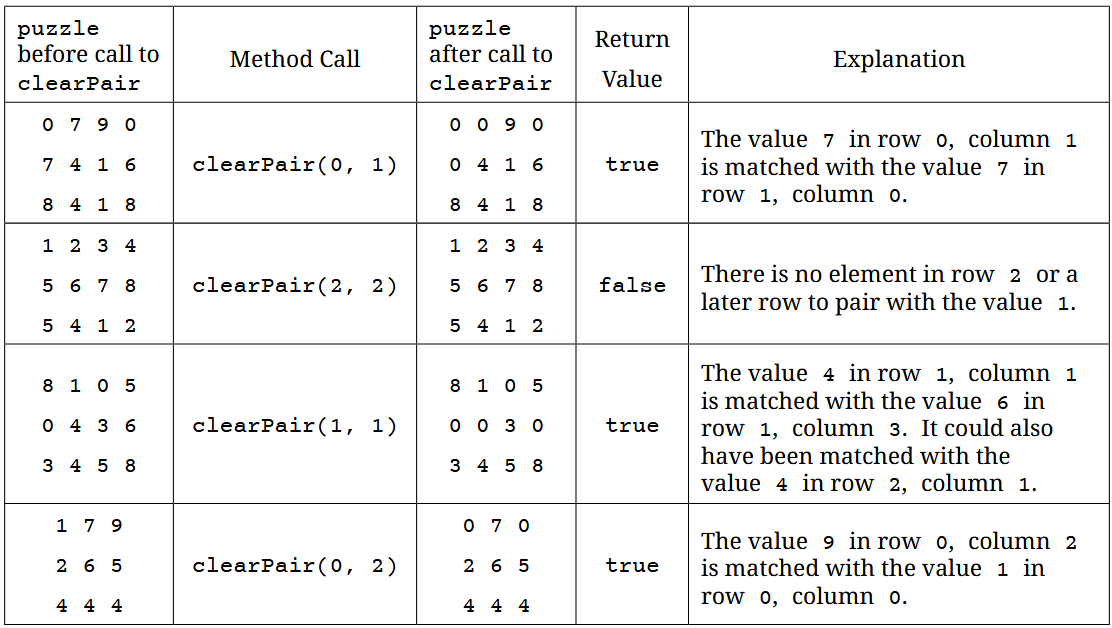
Walkthrough of Part B:
This method attempts to clear the selected cell by pairing it with another valid cell in the grid.
Starting from the given position:
- The method searches for another cell whose row index is greater than or equal to the given row.
- A valid partner must either have the same value or produce a sum of
10with the original cell.
If a valid partner is found:
- Both cells are cleared.
- The method reports success.
If no partner exists:
- The grid remains unchanged.
- The method reports failure.
The order in which the grid is searched matters, but any valid match is acceptable.
Example Reasoning
When the method is called on a specific cell, its value becomes the reference point. The grid is scanned to locate a second cell that satisfies the pairing rules. Once such a cell is found, both values are removed from the puzzle.
Code Runner Challenge
Write the constructor for the SumOrSameGame class. Then, complete method clearPair
View IPYNB Source
// CODE_RUNNER: Write the constructor for the SumOrSameGame class. Then, complete method clearPair
public class SumOrSameGame
{
private int[][] puzzle;
/**
* Creates a two-dimensional array and fills it with random integers,
* as described in part (a)
* Precondition: numRows > 0; numCols > 0
*/
public SumOrSameGame(int numRows, int numCols)
{ /* to be implemented in part (a) */ }
/**
* Identifies and clears an element of puzzle that can be paired with
* the element at the given row and column, as described in part (b)
* Preconditions: row and col are valid row and column indices in puzzle.
* The element at the given row and column is between 1 and 9, inclusive.
*/
public boolean clearPair(int row, int col)
{ /* to be implemented in part (b) */ }
/* There may be instance variables, constructors, and methods that are not shown. */
}
// Runner: Do Not Edit
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Game test starting...");
SumOrSameGame g = new SumOrSameGame(4, 4);
System.out.println("clearPair test: " + g.clearPair(0,0));
}
}
Main.main(null);
Scoring Guidelines
Part A
Solution:
The grid is built by first allocating the correct dimensions and then systematically visiting every position in the array.
By assigning a random value to each cell during traversal, the puzzle is fully initialized and ready for gameplay.
This approach guarantees:
- No cell is skipped
- All values fall within the required range
public SumOrSameGame(int numRows, int numCols)
{
puzzle = new int[numRows][numCols];
for (int row = 0; row < numRows; row++)
{
for (int col = 0; col < numCols; col++)
{
puzzle[row][col] = (int)(Math.random() * 9) + 1;
}
}
}
Guidelines:
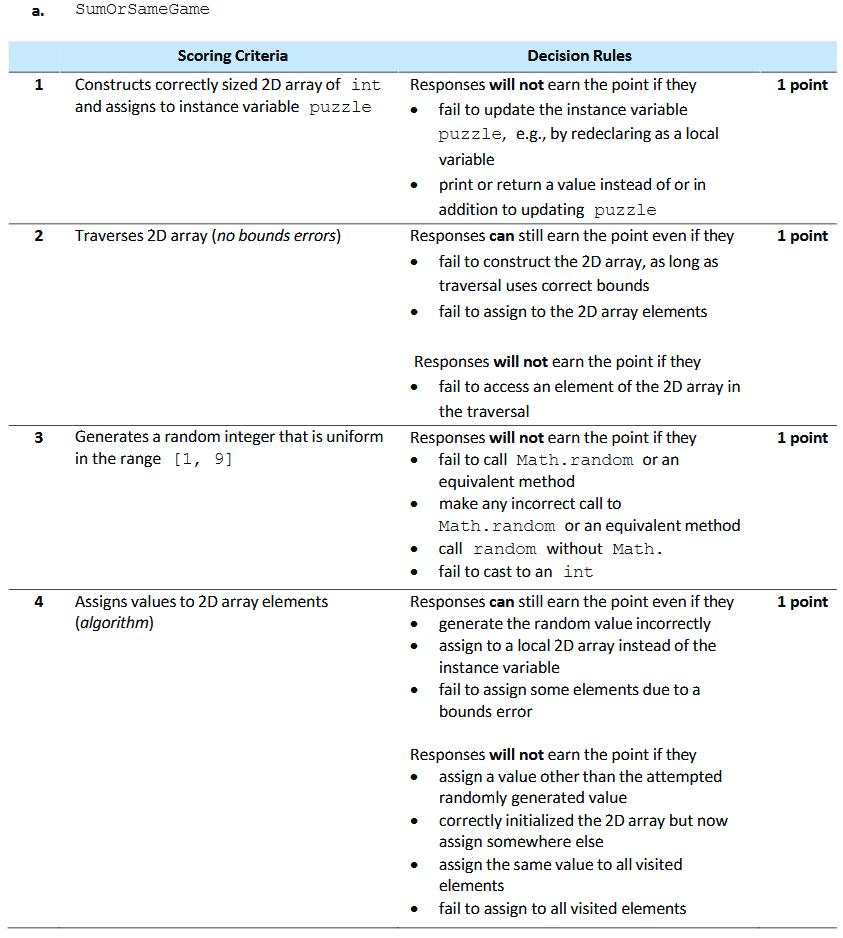
Part B
Solution:
The method follows a structured search pattern:
- Identify the starting cell.
- Examine all eligible cells below or on the same row.
- Stop as soon as a valid partner is found.
This guarantees correctness while avoiding unnecessary work.
Why This Strategy Is Effective
- Every valid candidate cell is checked.
- The puzzle state is only modified when a legal move exists.
- The method terminates immediately once its task is complete.
Common Errors
- Accidentally pairing a cell with itself.
- Clearing only one of the two cells.
- Modifying the grid when no valid partner exists.
- Searching outside the allowed row range.
public boolean clearPair(int row, int col)
{
int val1 = puzzle[row][col];
for (int currRow = row; currRow < puzzle.length; currRow++)
{
for (int currCol = 0; currCol < puzzle[0].length; currCol++)
{
int val2 = puzzle[currRow][currCol];
if (currRow != row || currCol != col)
{
if (val1 == val2 || val1 + val2 == 10)
{
puzzle[row][col] = 0;
puzzle[currRow][currCol] = 0;
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
Guidelines:

